-
[Design Pattern] Composite PatternLearn/Architecture 2022. 9. 25. 01:16
# 개요
계층(Hierarchy)이 있는 객체들을 동일하게 다루기 위해 사용하는 패턴
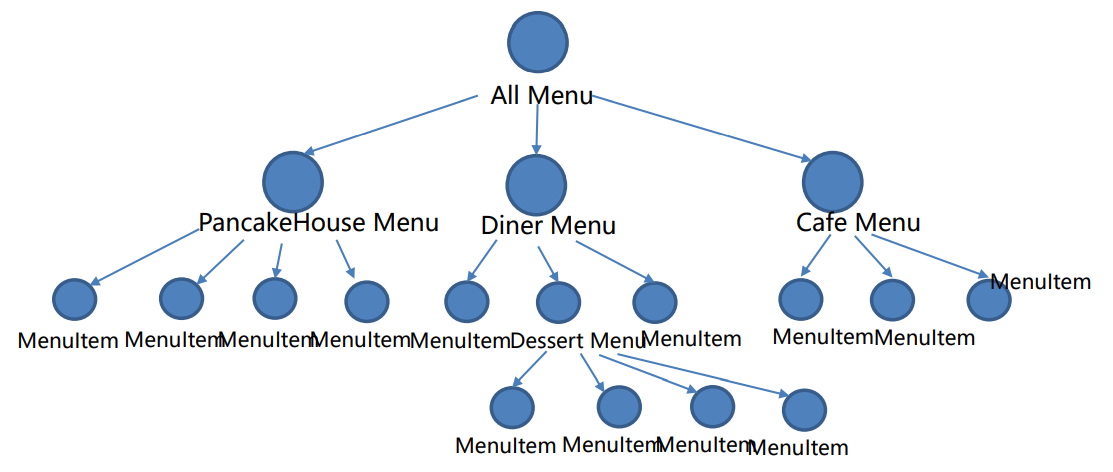
위와 같이 계층이 있을 경우 아래와 같이 계층에 따라 다르게 핸들링하지 않기 위한 패턴이다.
if ( current instanceOf(MenuItem)) // … handle Menu Item in a way else if (o instanceOf(Menu)) // … handle Menu in another way# Composite Pattern
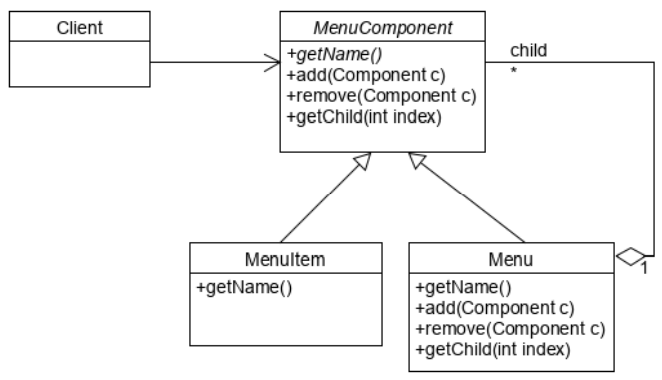
아래와 같이 Decorator Pattern과 유사하게 디자인 할 수 있다.
- 클라이언트는 MenuComponent를 통해 MenuItem과 Menu에 동일하게 접근할 수 있다.
- Decorator Pattern처럼 Association, Inheritance를 모두 가지고 있다.
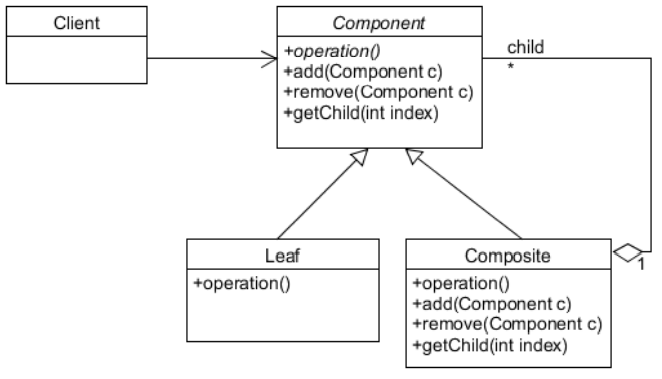
일반화하면 다음과 같다.
- 자식이 없는건 Leaf로 표현한다.
# 예시 코드
Component Class
- Component는 인터페이스의 역할만 할 뿐 그 자체의 인스턴스는 의미가 없으므로 예시에서는 다 exception 처리
public class MenuComponent { public void add(MenuComponent menuComponent) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public void remove(MenuComponent menuComponent) { .... }Leaf Class
public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent { String name; String description; .... // 예시에서는 이 메서드만 비교 public void print() { System.out.print(" " + getName()); if (this.isVegetarian()) System.out.println("(v)"); System.out.println(", " + getPrice()); System.out.println(" --" + getDescription()); } }Composite Class
- menuComponents에 자식들을 담는다.
- print시 자식들을 하나씩 꺼내며 반복
- 자식을 꺼낼 때 상위 인터페이스의 함수를 호출하므로 타입은 Leaf인지 Composite인지 신경 쓸 필요가 없음 (polymorphism)
public class Menu extends MenuComponent { // 자식들을 담음 ArraryList menuComponents = new ArrayList(); String name; String description; .... public void print() { // 자기 자식을 하나씩 꺼내면서 출력함 Iterator iterator = menuComponents.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { // 자식의 타입은 신경 쓸 필요가 없음 MenuComponent menuComponent = (MenuComponent)iterator.next(); menuComponent.print(); } } }# 트리 구조를 위한 Iterator
아래와 같은 트리 구조의 경우 위 코드의 iterator 방식이 작동하지 않는다.
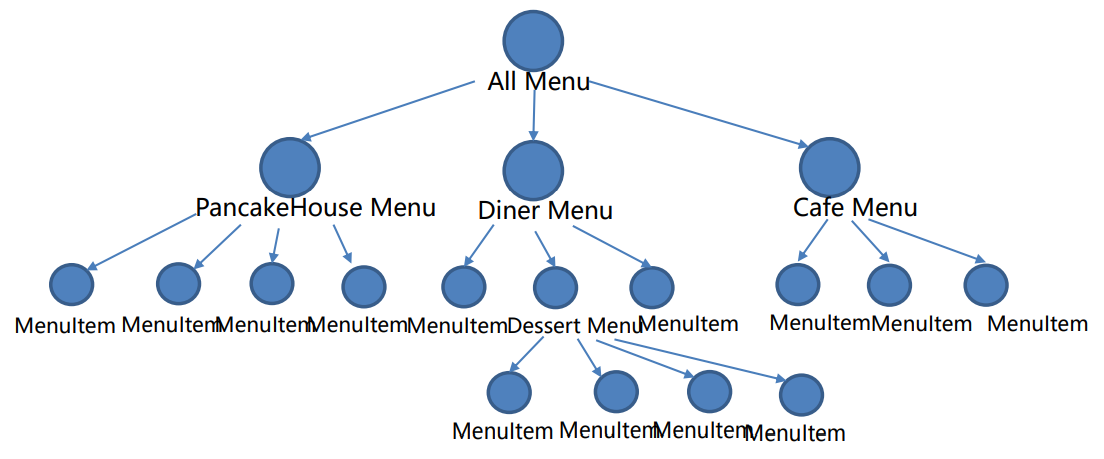
만약 전체 트리를 순회하는 Iterator를 만들 수 있다면 아래와 같이 특정 메뉴를 찍는 작업도 할 수 있다.
public class Waitress { MenuComponent allMenus; public Watiress(MenuComponent allMenus) { this.allMenus = allMenus; } public void printMenu() { allMenus.print(); } public void printVegetarianMenu() { // 전체 트리를 순회하는 Iterator Iterator iterator = allMenus.createIterator(); System.out.println("\nVEGETARIAN MENU\n-------"); while (iterator.hasNext()) { MenuComponent menuComponent = (MenuComponent)iterator.next(); try { if (menuComponent.isVegetarian()) menuComponent.print(); } catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {} } } }전체 Iterator를 순회하는 코드는 아래와 같이 작성할 수 있다.
- 자식이 있는 Comosite에서는 Iterator를 반환한다.
- 자식이 없는 Leaf는 동일한 타입으로 일관성 있게 핸들링하기 위해 NullIterator를 사용한다.
public class Menu extends MenuComponent { Iterator iterator = null; // other code here doesn't change public Iterator createIterator() { if (iterator == null) iterator = new CompositeIterator(menuComponents.iterator()); return iterator; } } public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent { // other code here doesn't change public Iterator createIterator() { return new NullIterator(); } }# 고려할 점
add(), remove(), getchild() 같은 자식을 다루는 메서드는 어디에 있어야 적절한가?
- 어떤 것을 중요시 하냐에 따라 두 가지 옵션이 있다.

왼쪽은 위의 예시에서 사용한 방법으로 Transparency를 중요시 하는 구현 방식이다.
- 장점은 모든 컴포넌트를 같은 방식으로 다룰 수 있다.
- 단점은 Component에서 Leaf에 없는 operation에 접근을 하는 것에 대해 Exception을 구현해줘야 한다.
- 컴파일 타임에는 확인할 수가 없고 런타임때 확인할 수 있다.
오른쪽은 Safety를 중요시 하는 구현 방식으로 공통된 operation만 Component에 구현한다.
- 장점은 Leaf에 없는 operation에 대해 접근하는 것을 컴파일 타임때 탐지할 수 있다.
- 단점은 더 이상 Leaf와 composite를 같은 방식으로 접근할 수 없다.
# 관련된 패턴
## Composite vs Decorator
공통점 - 구조적으론 비슷하다.
- 상위 타입으로 자식에 접근하며 recursive하게 만들 수 있다.
차이점 - 의도가 다르다.
- Decorator Pattern은 이미 존재하는 객체에 새로운 책임을 부여하기 위해 감싼다.
- Composite Pattern은 트리 모양의 hierarchy를 표현하는데 초점을 맞추고 있다.
둘 다 비슷하므로 혼용하는 경우가 많이 있다.
## Iterator Pattern
아래의 자료구조를 노출하지 않으면서 object의 element에 접근하기 위한 패턴으로 Composite Pattern과 유사하다.
# 정리
Composite Pattern은 트리 모양의 구조를 표현하고 전체 계층(hierarchy)를 표현할 수 있다.
클라이언트는 개별 오브젝트를 구분하지 않고 접근할 수 있다. (Leaf, Composite)
'Learn > Architecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Design Pattern] MVC Pattern (0) 2022.09.25 [Design Pattern] Bridge Pattern (0) 2022.09.25 [Design Pattern] Decorator Pattern (0) 2022.09.24 [Design Pattern] Adapter Pattern (0) 2022.09.04 [Design Pattern] Singleton Pattern (0) 2022.08.31